The European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) will be held in Milan, Italy, from September 29 to October 4, 2024. At this year's conference, the paper titled "LTRL: Boosting Long-Tail Recognition via Reflective Learning," authored by Professor Zhang Fan’s team from the School of Information Science and Technology, has been selected for an oral presentation.
This year, ECCV received 8,585 valid submissions worldwide and accepted 2,395 papers, of which 188 were chosen for oral presentations, with a selection rate of 2.1%. This paper marks the first oral presentation from our university at ECCV.
Research Findings
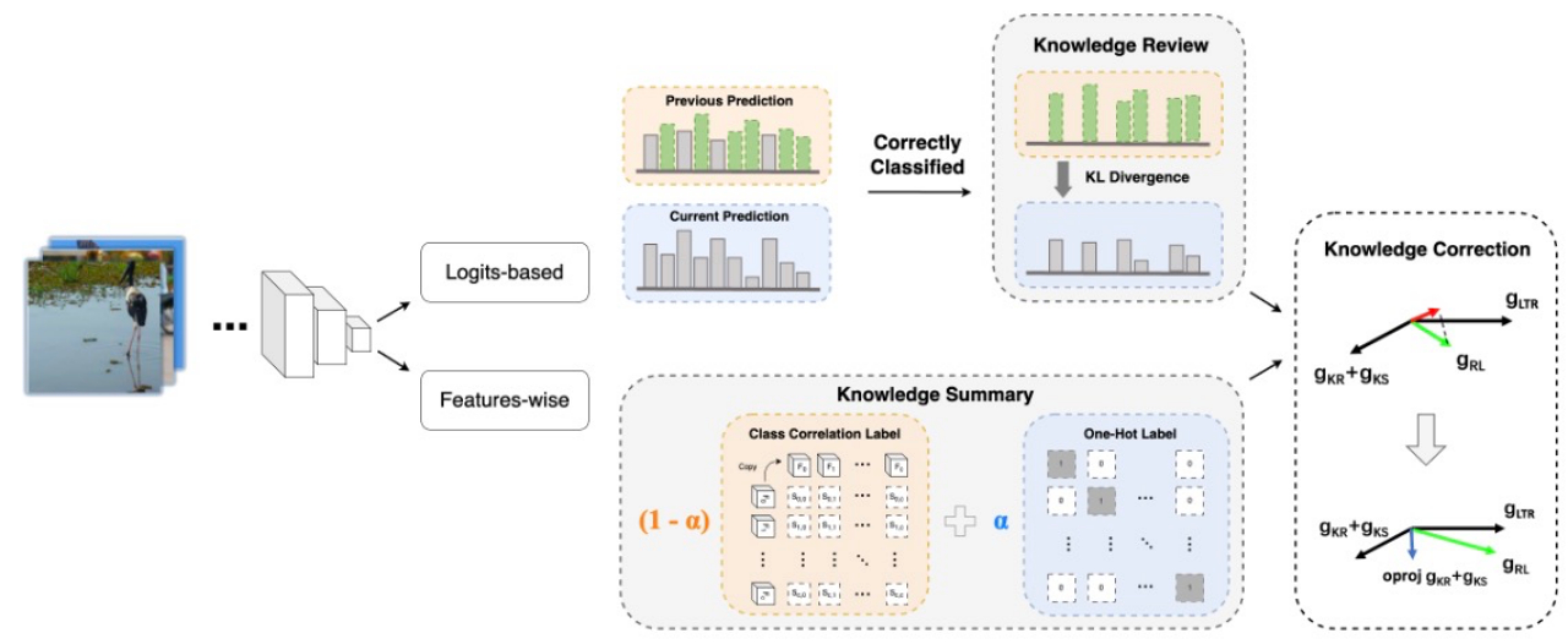
Figure 1: The framework of the method
In real-world scenarios, knowledge distributions often exhibit a long-tail pattern. Humans manage to better grasp knowledge across such imbalanced distributions by reviewing, summarizing, and correcting errors. Inspired by this learning process, the authors propose a novel learning paradigm, called Reflective Learning, to tackle long-tail recognition problems. The method integrates three processes: reviewing past predictions during training, summarizing and utilizing learned feature relationships between classes, and correcting gradient conflicts arising from different learning methods. These modules are designed to be plug-and-play, enabling seamless integration with existing long-tail learning methods. The proposed approach has achieved state-of-the-art performance across multiple popular long-tail visual benchmarks.
Conclusion and Outlook
Reflective Learning, proposed in this paper, effectively addresses long-tail distribution problems through knowledge review, summarization, and correction, and can be easily integrated with existing methods. Experimental results demonstrate leading performance in multiple visual benchmarks, validating its efficacy in long-tail recognition. Future research could further explore its application in other complex tasks and domains, and optimize its core processes to enhance performance across different model architectures. By integrating with other advanced technologies, Reflective Learning has the potential to yield more breakthrough results.
Author Information
The first author of the paper is Zhao Qihao, a Ph.D. student from the class of 2021 at the School of Information Science and Technology. The co-first author is Dai Yalun, a 2018 undergraduate alumnus, under the supervision of Professor Zhang Fan and Associate Professor Hu Wei, in collaboration with Professor Liu Jun from Lancaster University. Beijing University of Chemical Technology is the primary institution for this research.
Corresponding Author Biography
Zhang Fan is a professor at the School of Information Science and Technology/Artificial Intelligence Center at Beijing University of Chemical Technology, a member of the university's Academic Degree Committee, and a senior member of the Chinese Institute of Electronics/IEEE. He joined the university in 2010, with visiting research stints at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the Technical University of Dresden. His main research interests include remote sensing image processing and artificial intelligence. He has led over 30 projects, including those funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and has published more than 100 academic papers in ISPRS P&RS, IEEE TGRS, CVPR, ICCV, among others, with over 5,000 citations. He has received the Beijing Natural Science Second Prize and the Young Teaching Excellence Award from Beijing University of Chemical Technology.
